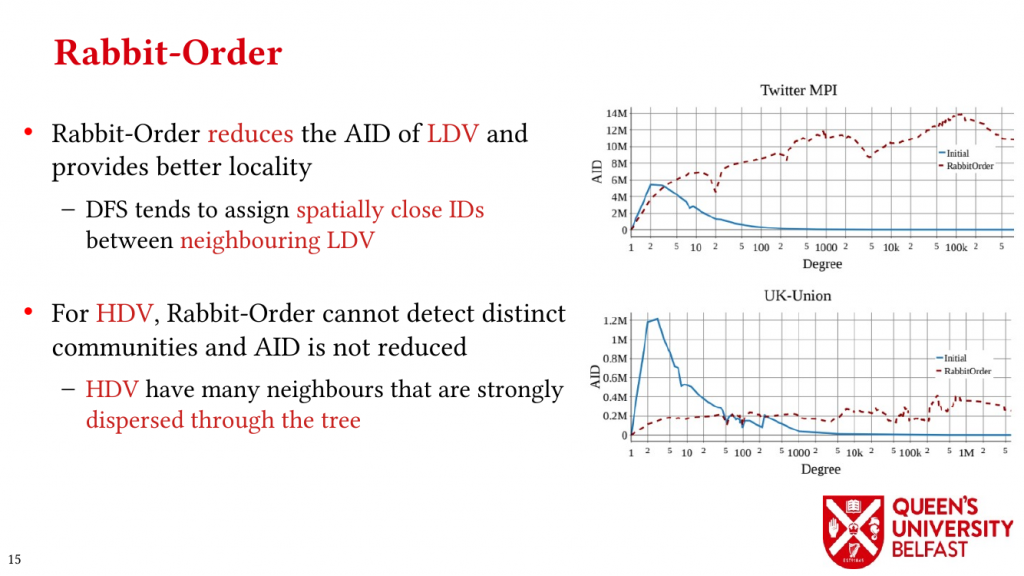
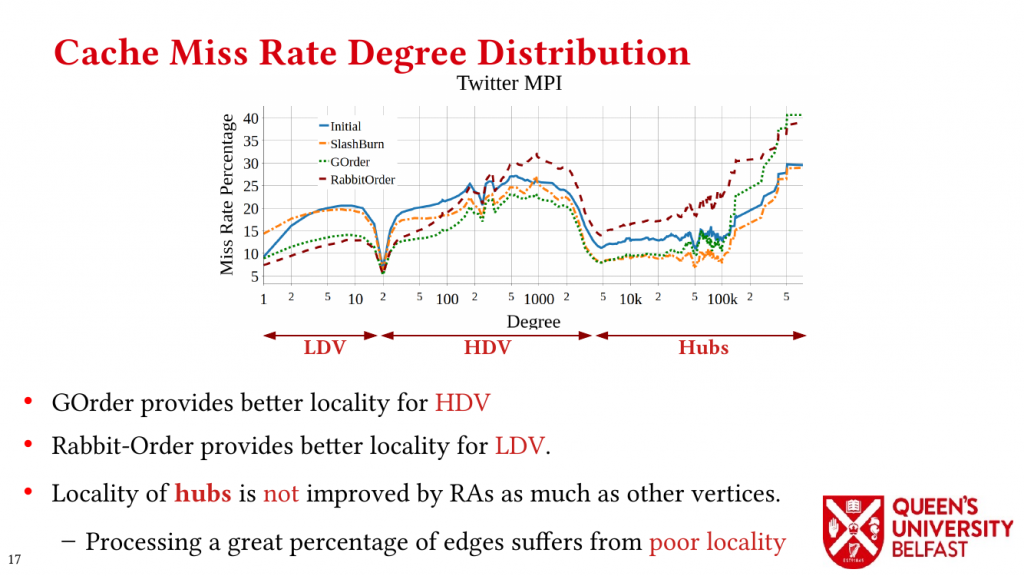
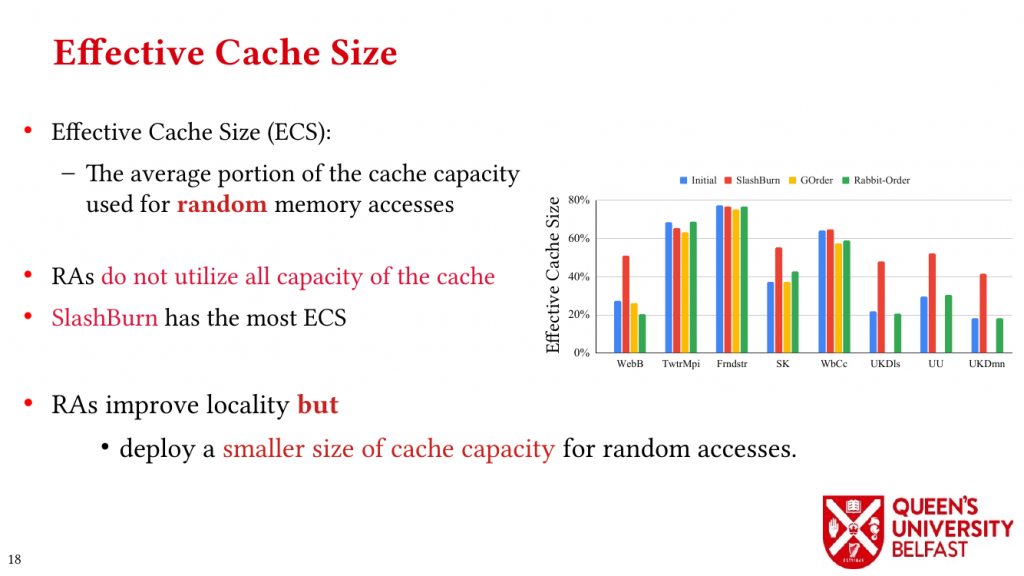
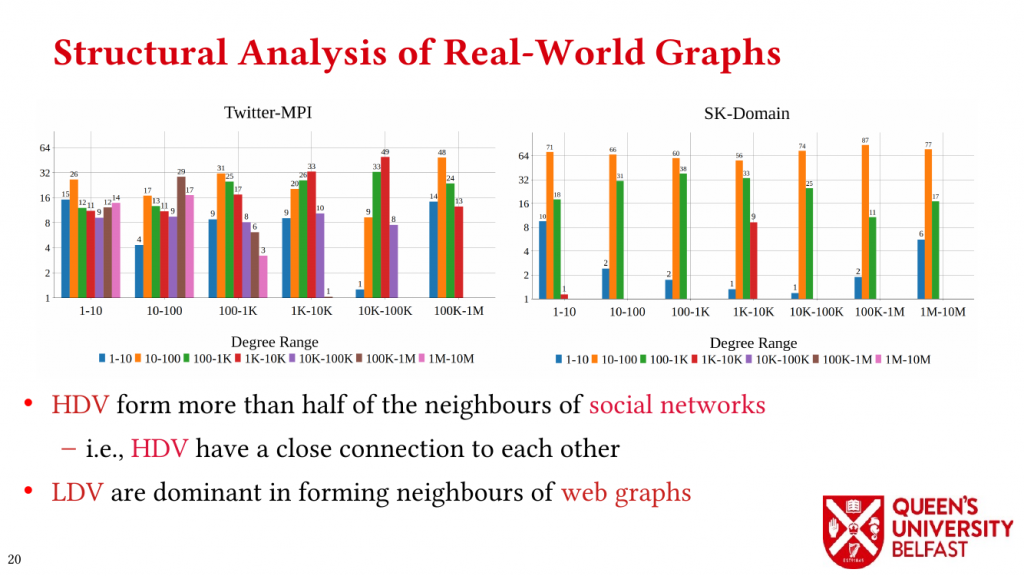
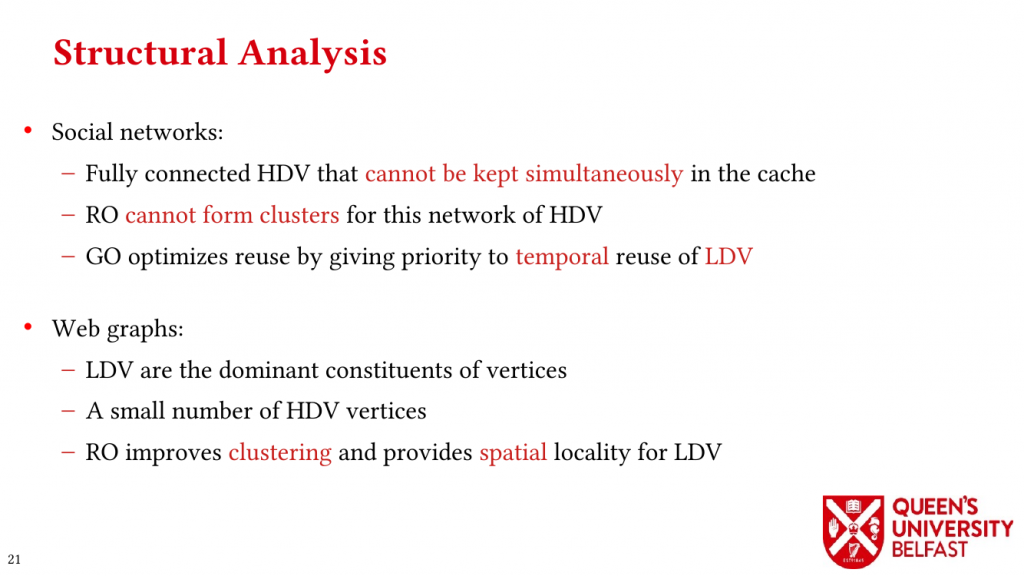
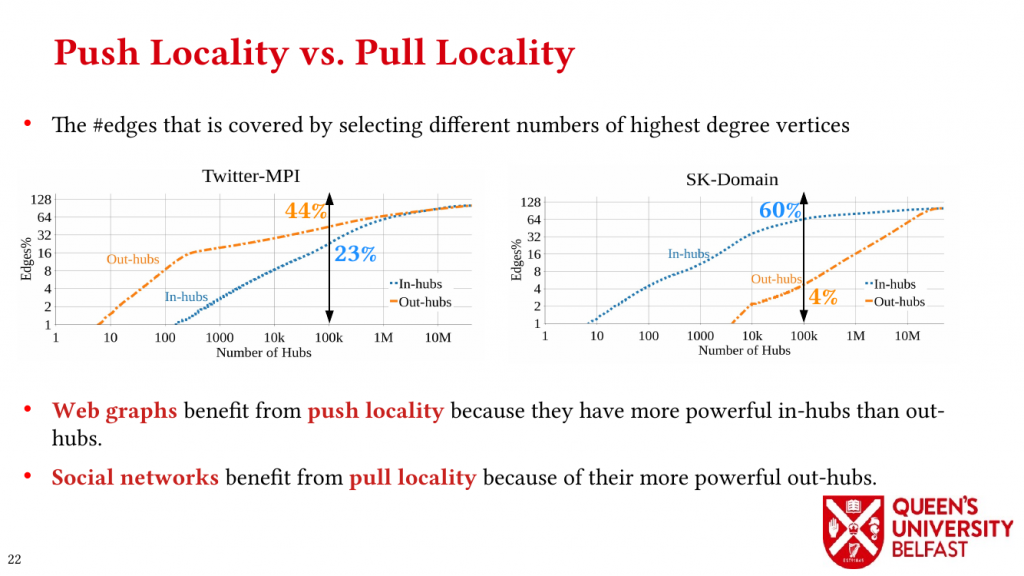
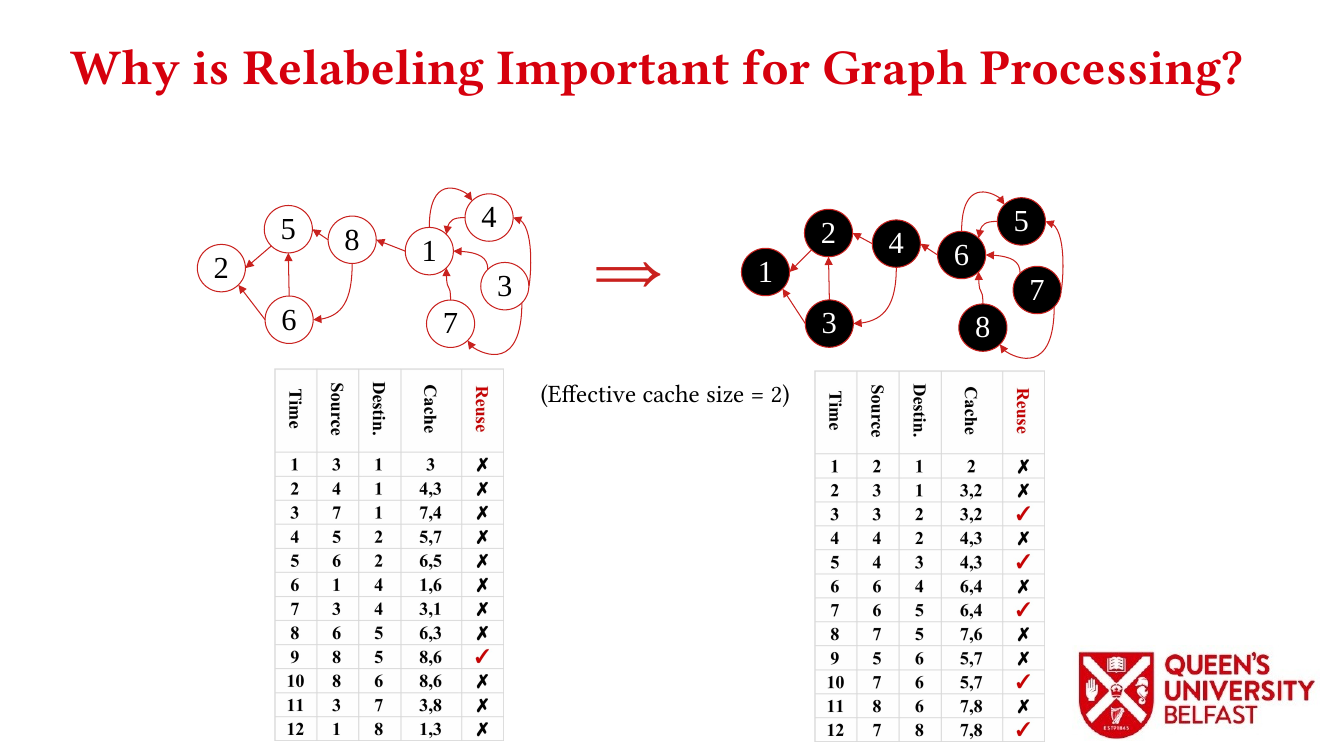
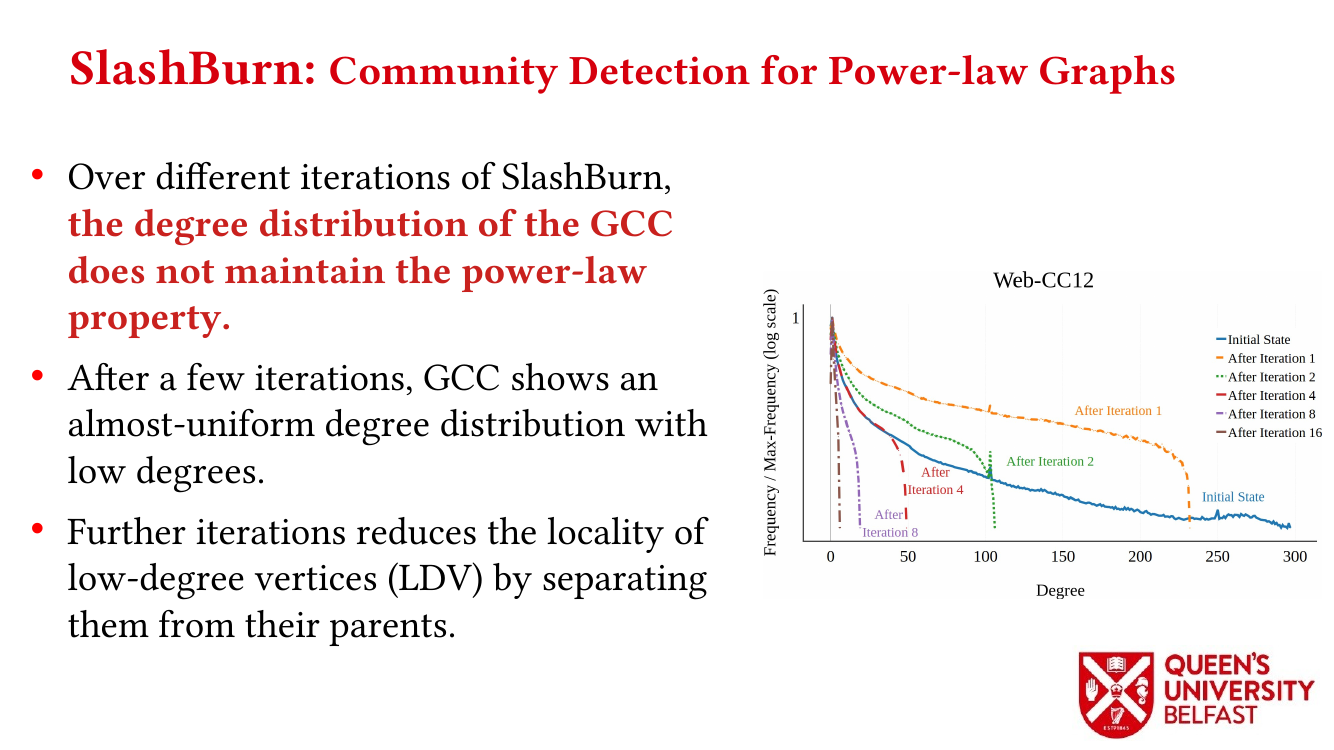
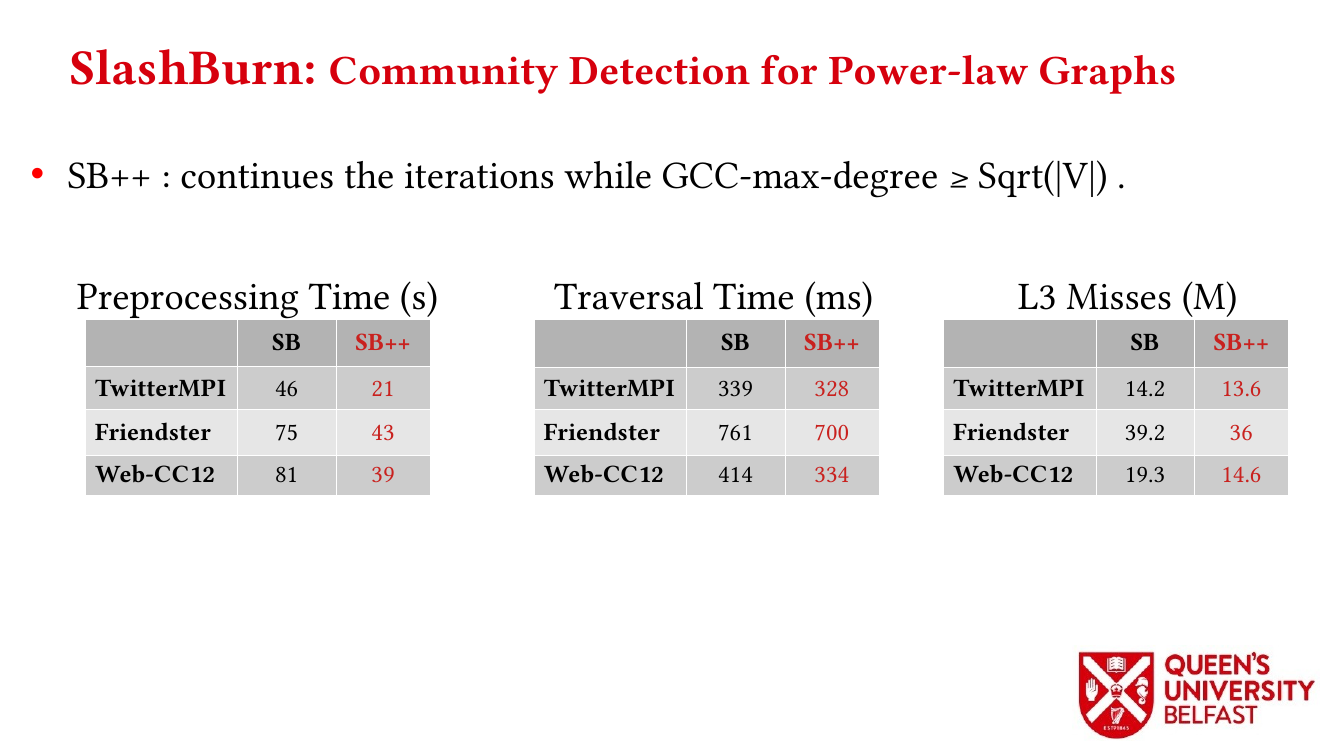
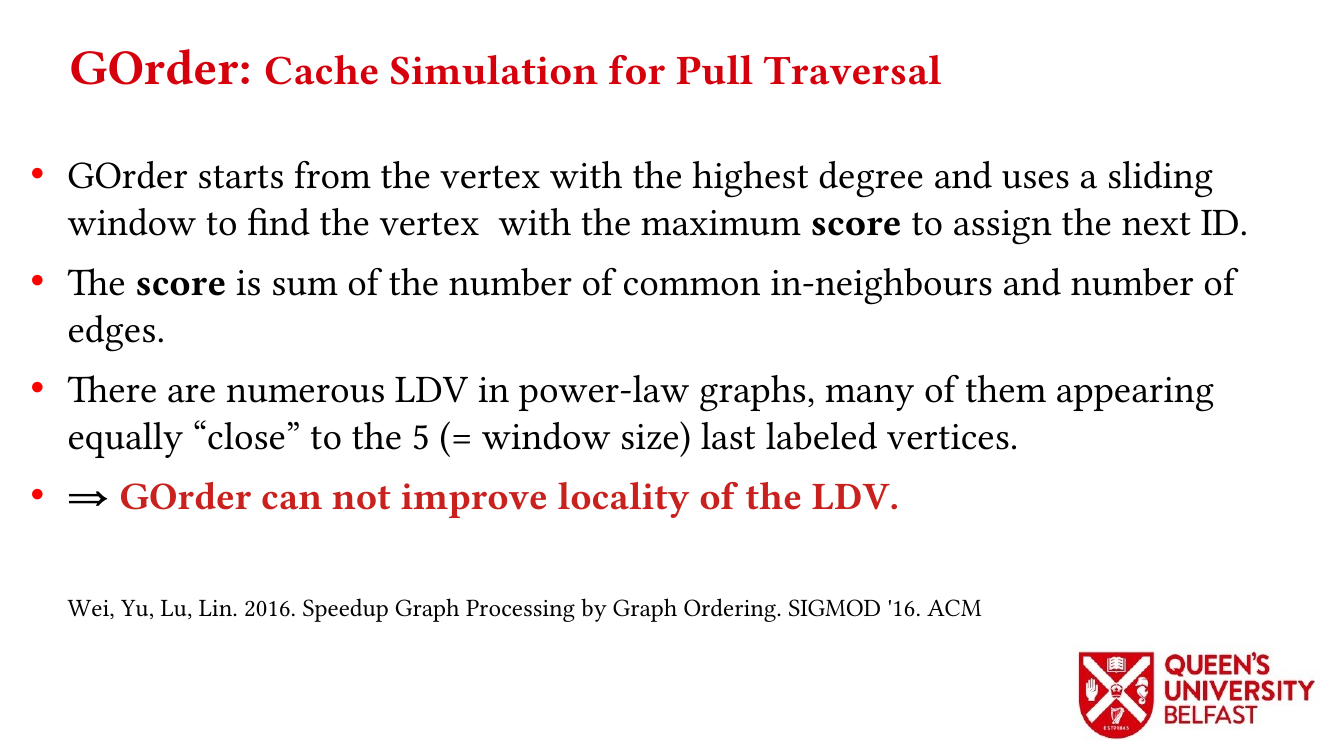
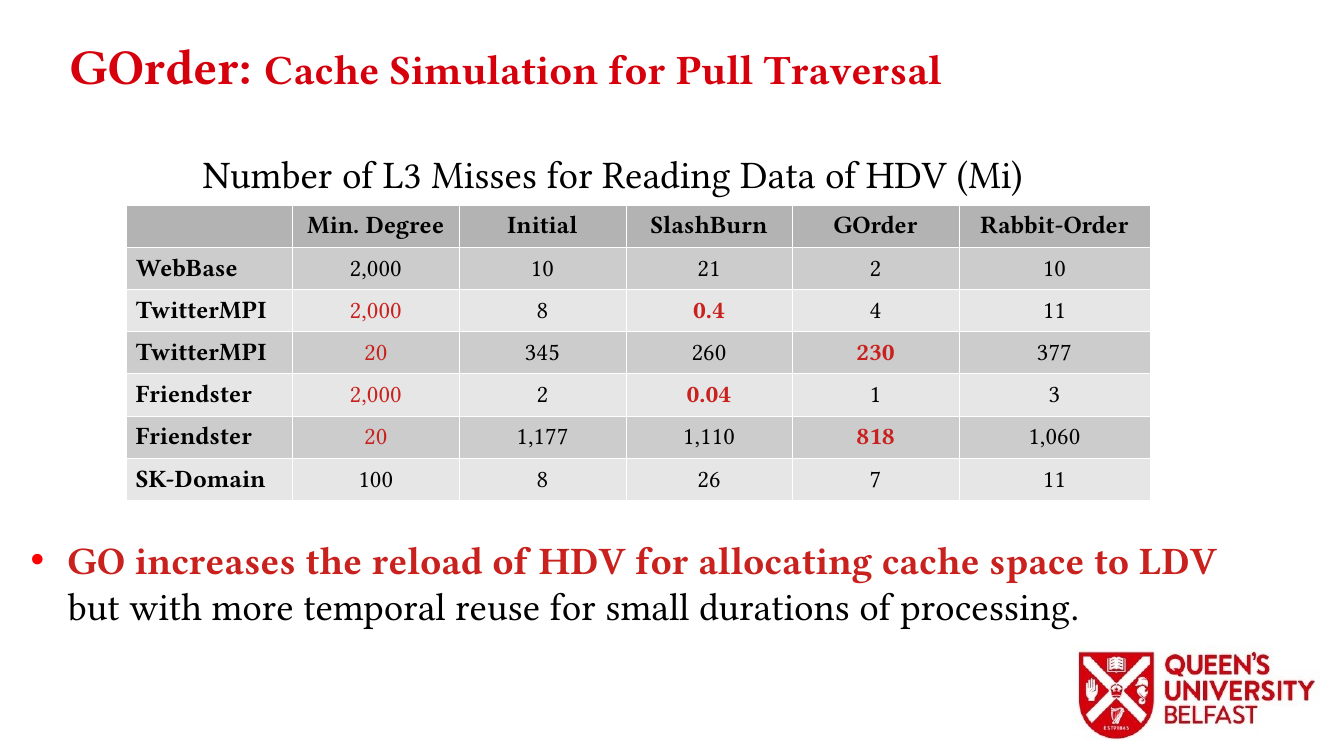
In applications such as graph processing, it is important how threads are pinned on CPU cores as the threads that share resources (such as memory and cache) can accelerate the performance by processing consecutive blocks of input dataset, especially, when the dataset has a high-level of locality.
In LaganLighter, we read the CPU topology to specify how OpenMP threads are pinned. In omp.c file, the block starting with comment “Reading sibling groups of each node“, reads the “/sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu*/topology/thread_siblings” files to identify the sibling threads and three arrays ("node_sibling_groups_start_ID“, “sibling_group_cpus_start_offsets“, and “sibling_groups_cpus“) are used to store the sibling CPUs.
Then, in block starting with comment “Setting affinity of threads“, the sibling groups are read and based on the total number of threads requested by user, a number of threads with consecutive IDs are pinned to sibling CPUs.
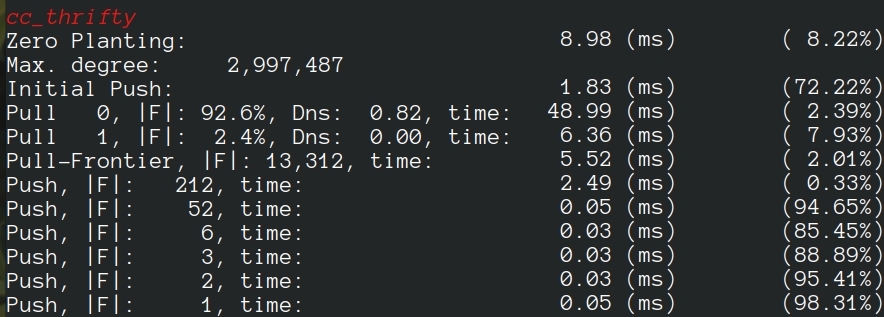
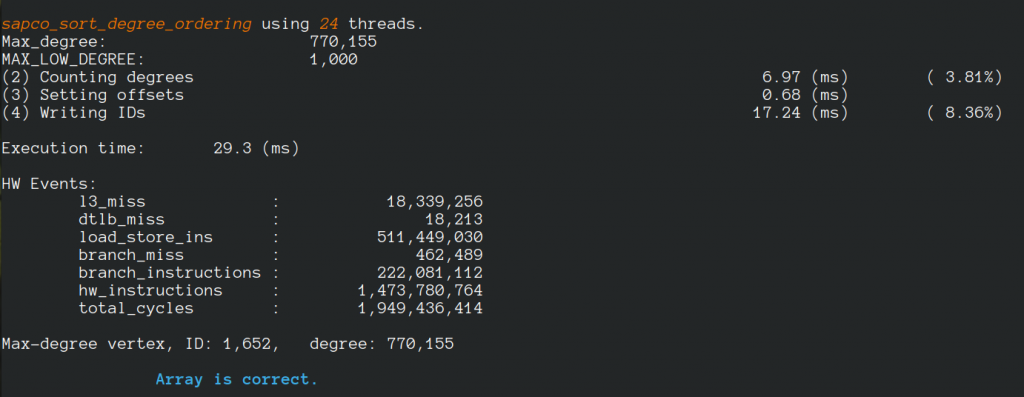
For a machine with 24 cores, 48 hyperthreads, when 48 threads are requested, we have:
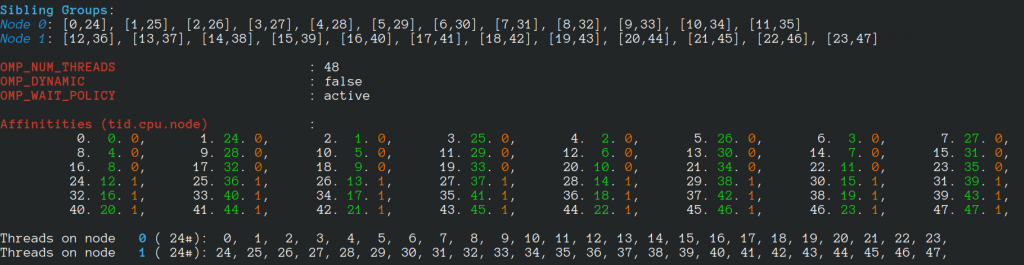
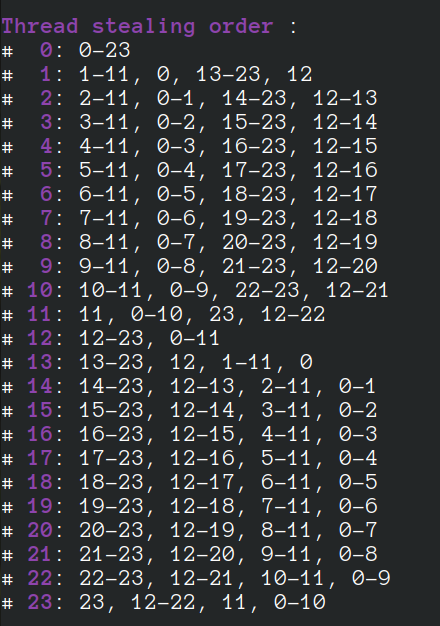
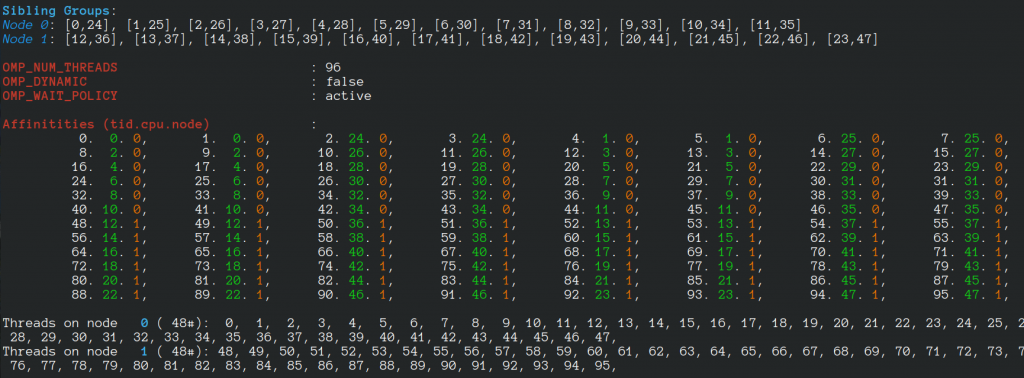
If 96 threads are created, we have:
- Random Vertex Relabelling in LaganLighter

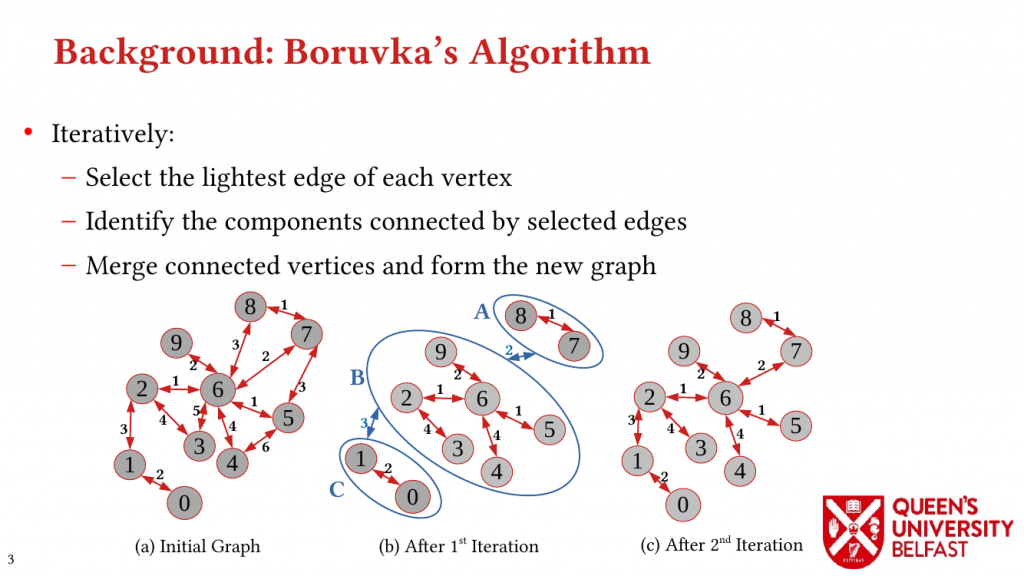
- Minimum Spanning Forest of MS-BioGraphs

- Topology-Based Thread Affinity Setting (Thread Pinning) in OpenMP

- An (Incomplete) List of Publicly Available Graph Datasets/Generators

- An Evaluation of Bandwidth of Different Storage Types (HDD vs. SSD vs. LustreFS) for Different Block Sizes and Different Parallel Read Methods (mmap vs pread vs read)

- SIMD Bit Twiddling Hacks

- LaganLighter Source Code

- On Optimizing Locality of Graph Transposition on Modern Architectures

- Random Vertex Relabelling in LaganLighter

- Minimum Spanning Forest of MS-BioGraphs

- Topology-Based Thread Affinity Setting (Thread Pinning) in OpenMP

- ParaGrapher Integrated to LaganLighter

- On Designing Structure-Aware High-Performance Graph Algorithms (PhD Thesis)

- LaganLighter Source Code

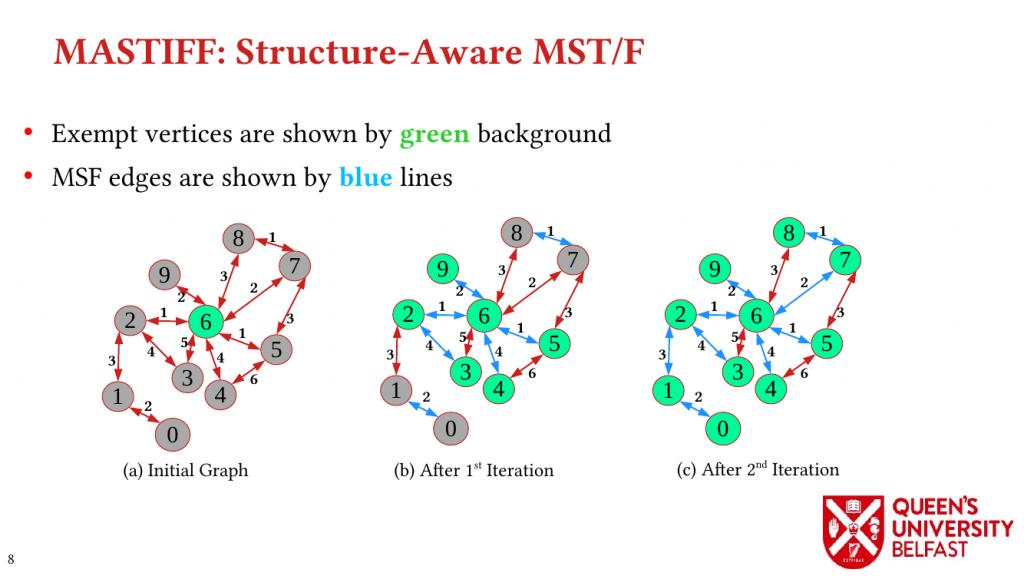
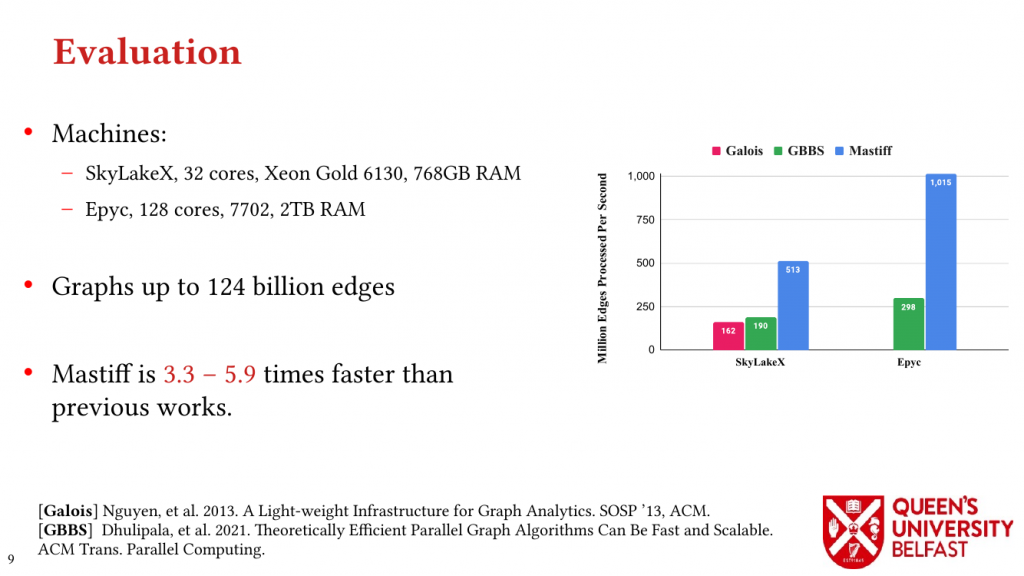
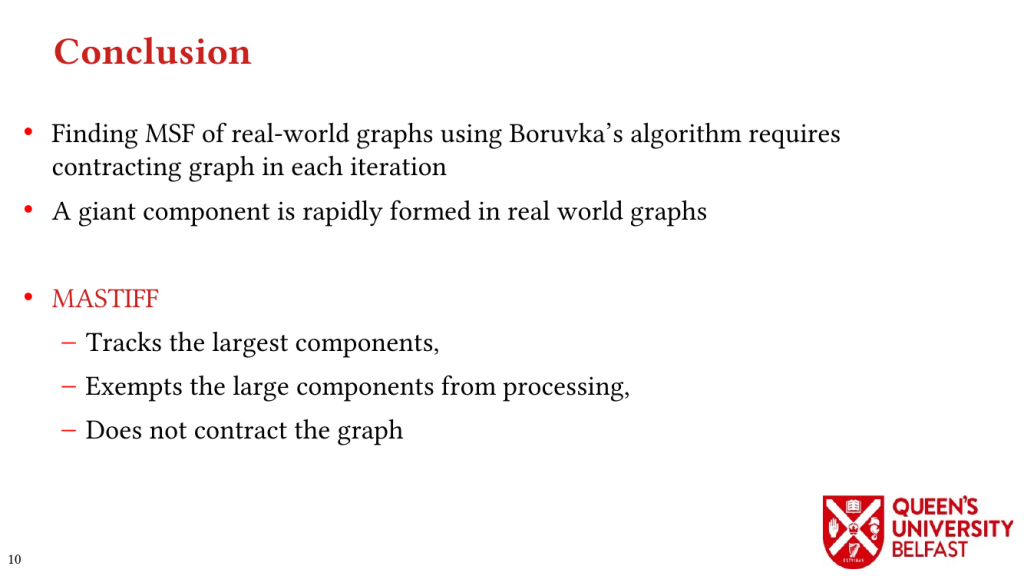
- MASTIFF: Structure-Aware Minimum Spanning Tree/Forest – ICS’22

- SAPCo Sort: Optimizing Degree-Ordering for Power-Law Graphs – ISPASS’22 (Poster)

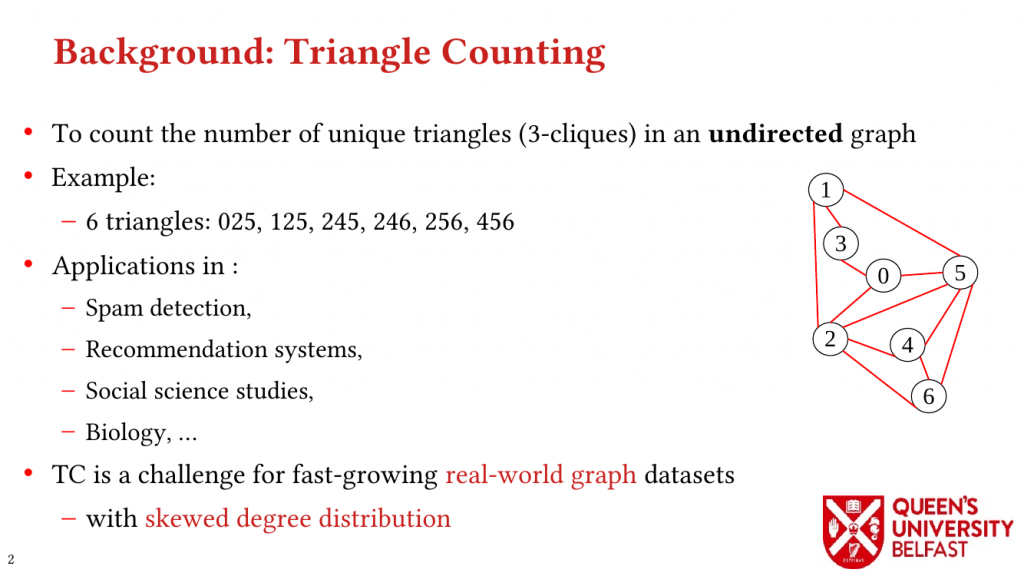
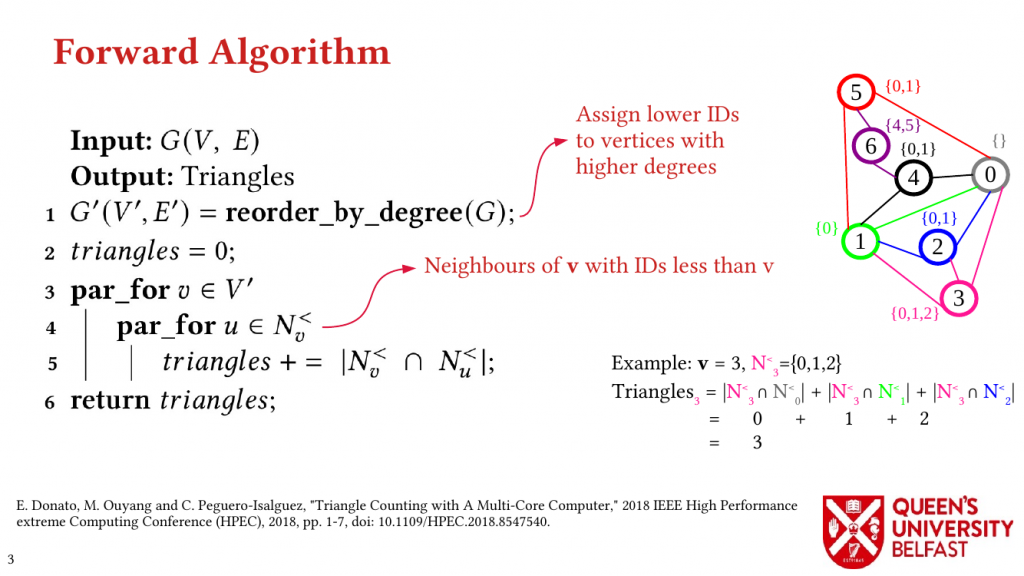
- LOTUS: Locality Optimizing Triangle Counting – PPOPP’22

- Locality Analysis of Graph Reordering Algorithms – IISWC’21

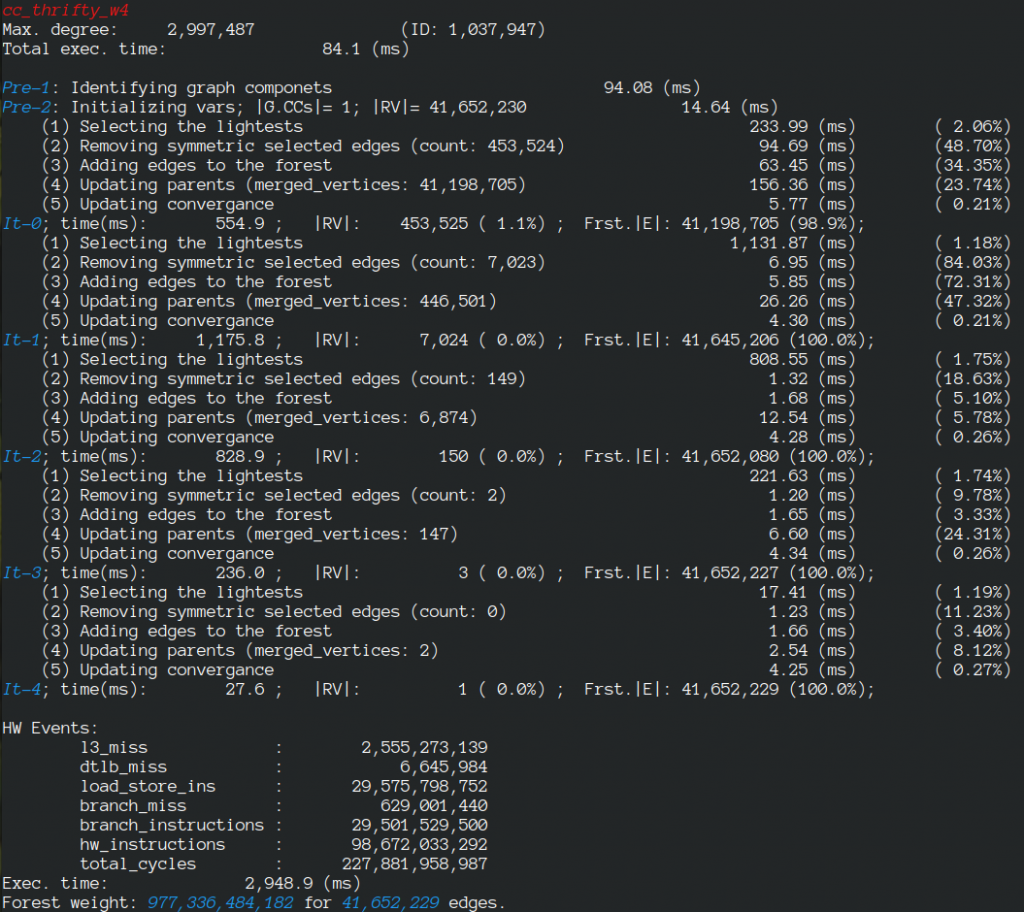
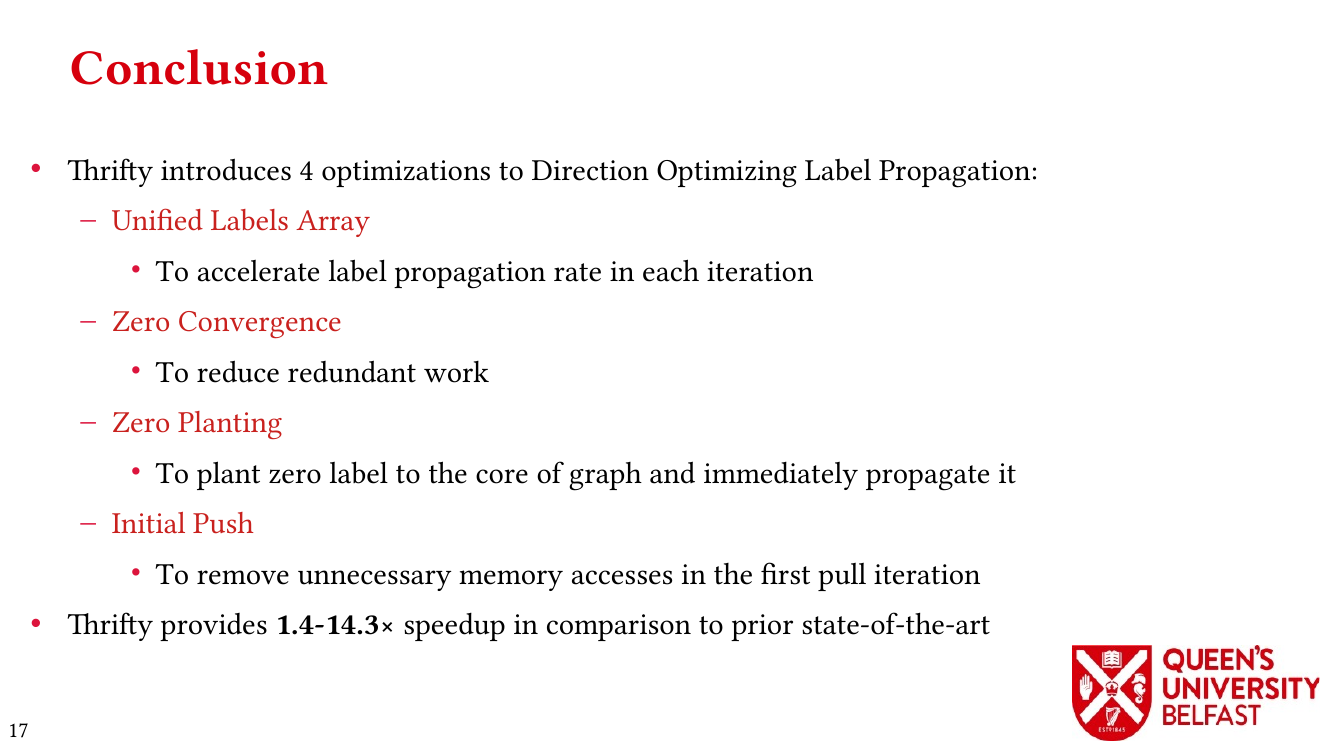
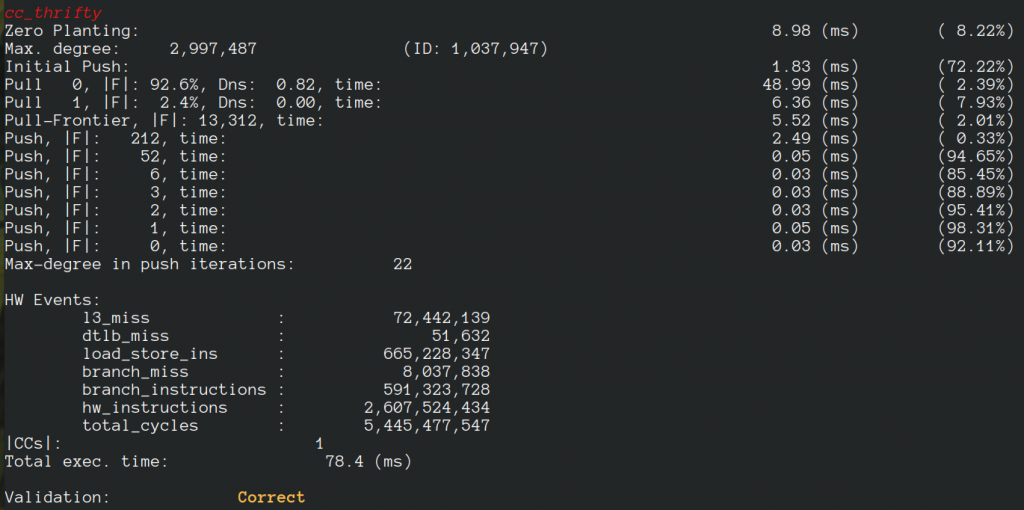
- Thrifty Label Propagation: Fast Connected Components for Skewed-Degree Graphs – IEEE CLUSTER’21

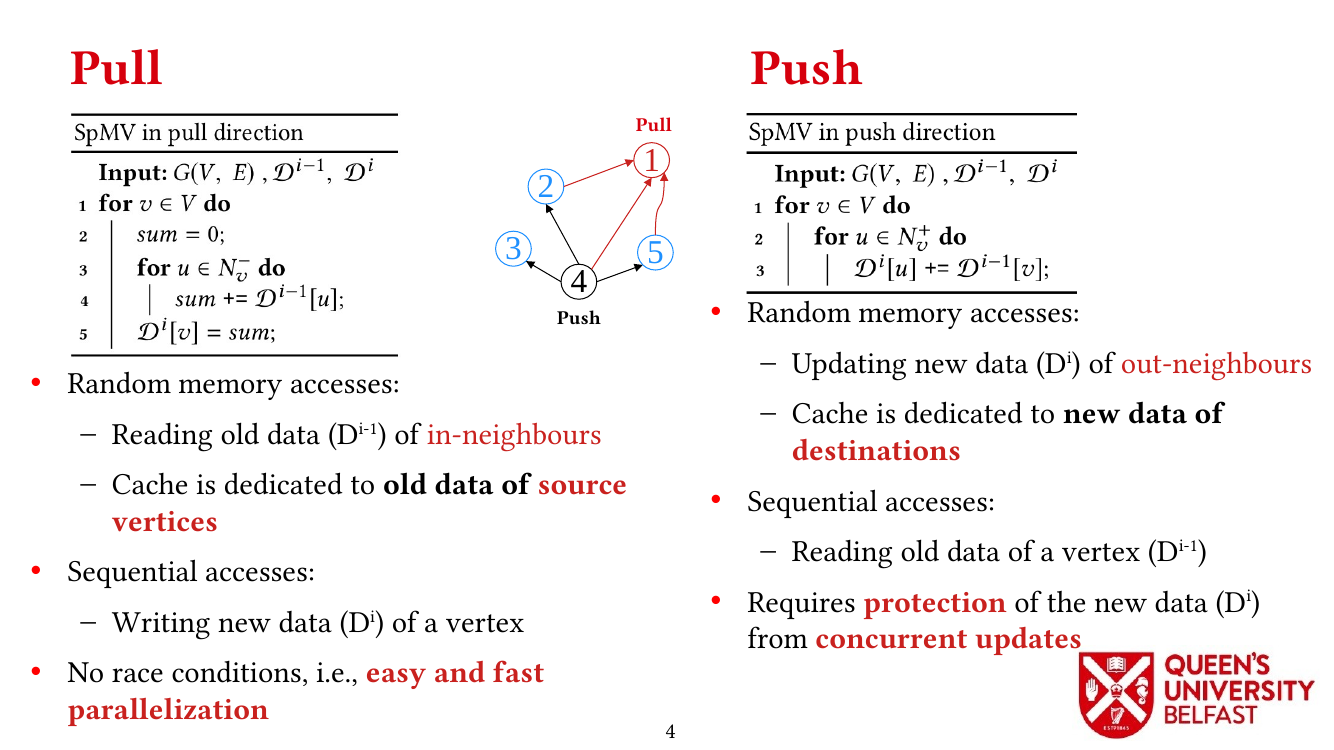
- Exploiting in-Hub Temporal Locality in SpMV-based Graph Processing – ICPP’21

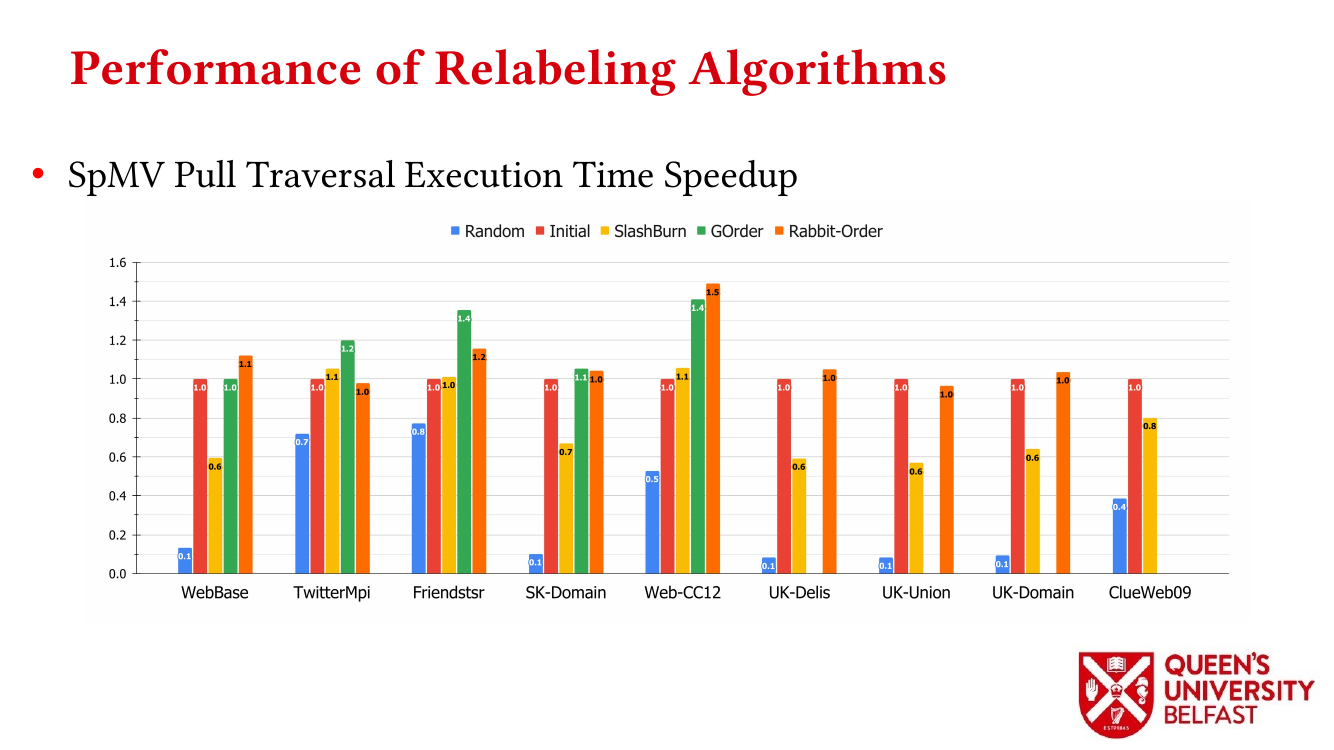
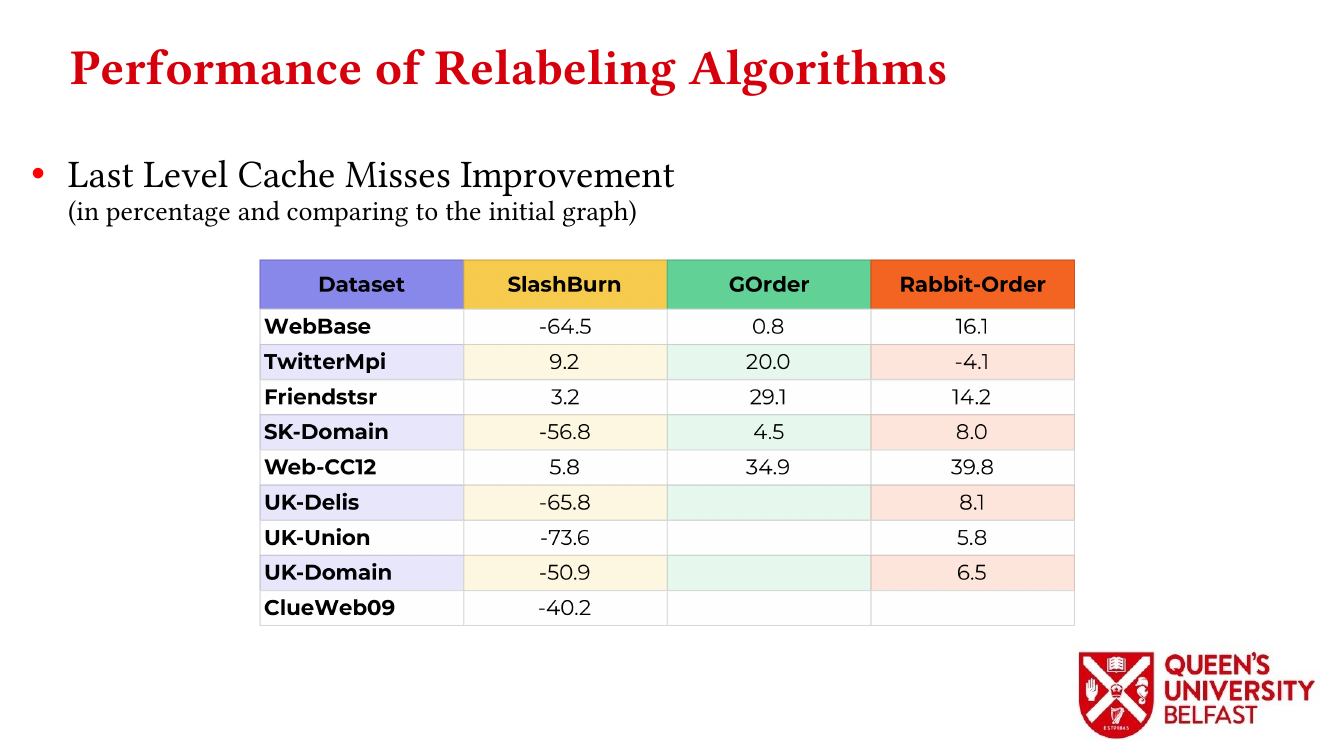
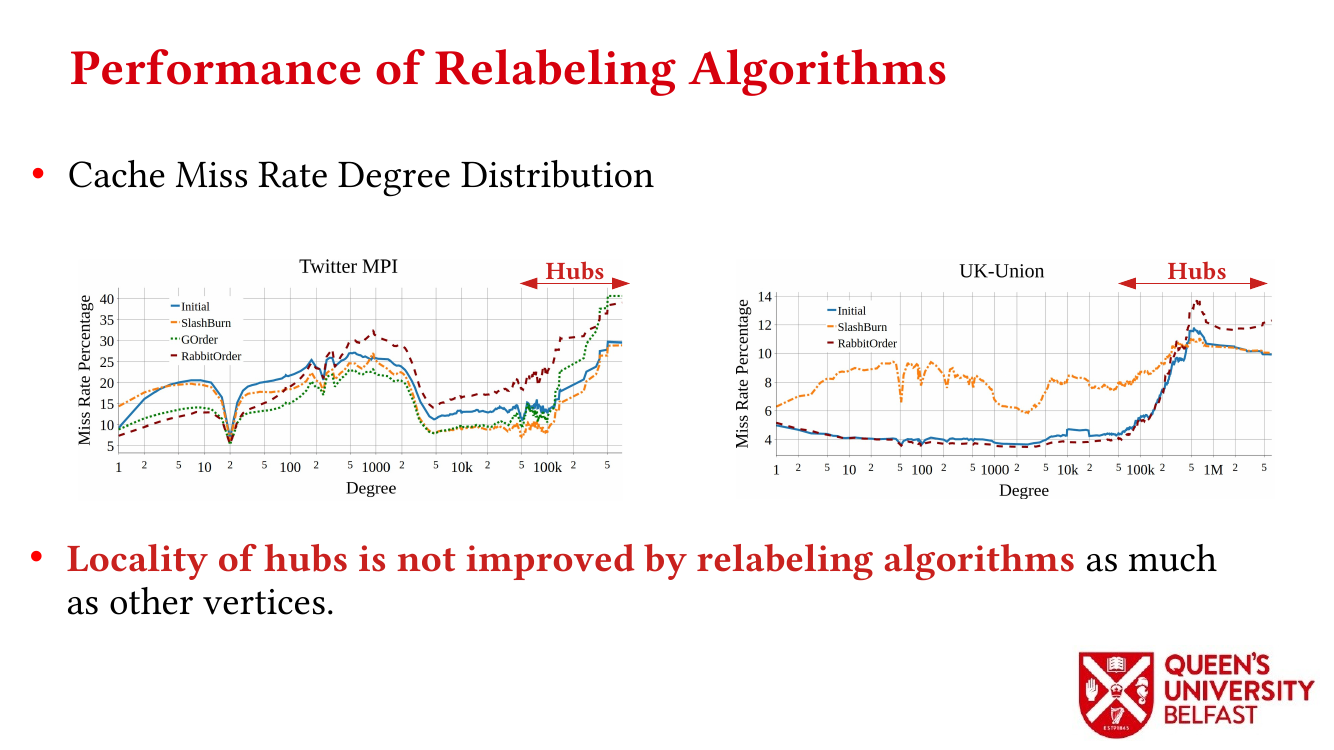
- How Do Graph Relabeling Algorithms Improve Memory Locality? ISPASS’21 (Poster)