27th ACM SIGPLAN Annual Symposium on Principles and Practice of Parallel Programming (PPoPP 2022)
April 2-6, 2022
Acceptance Rate: 31%
DOI: 10.1145/3503221.3508402
Authors’ Copy (PDF Format)
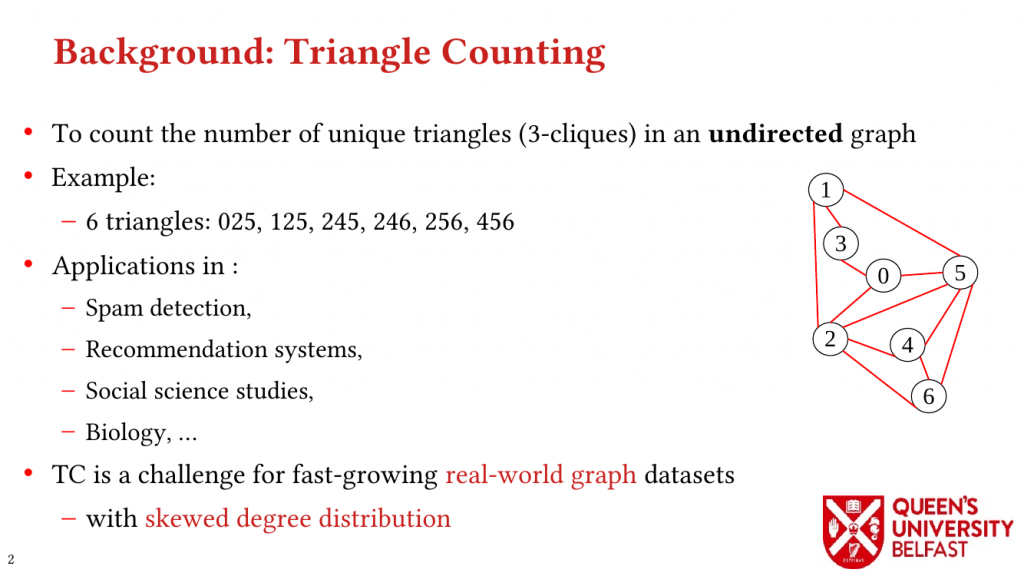
Triangle Counting (TC) is a basic graph algorithm and is widely used in different fields of science, humanities and technology. The great size of real-world graphs with skewed degree distribution is a prohibiting factor in efficient TC.
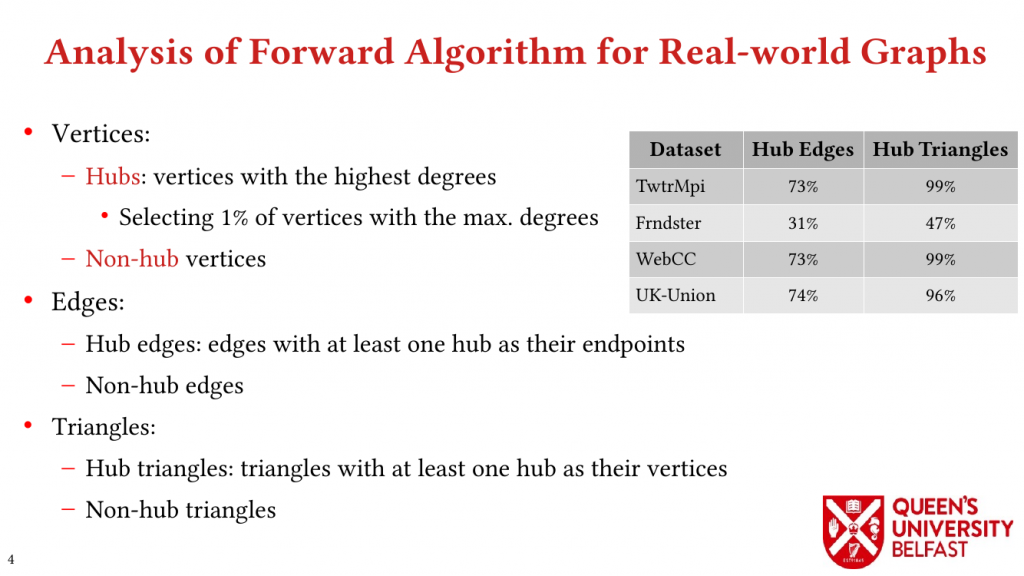
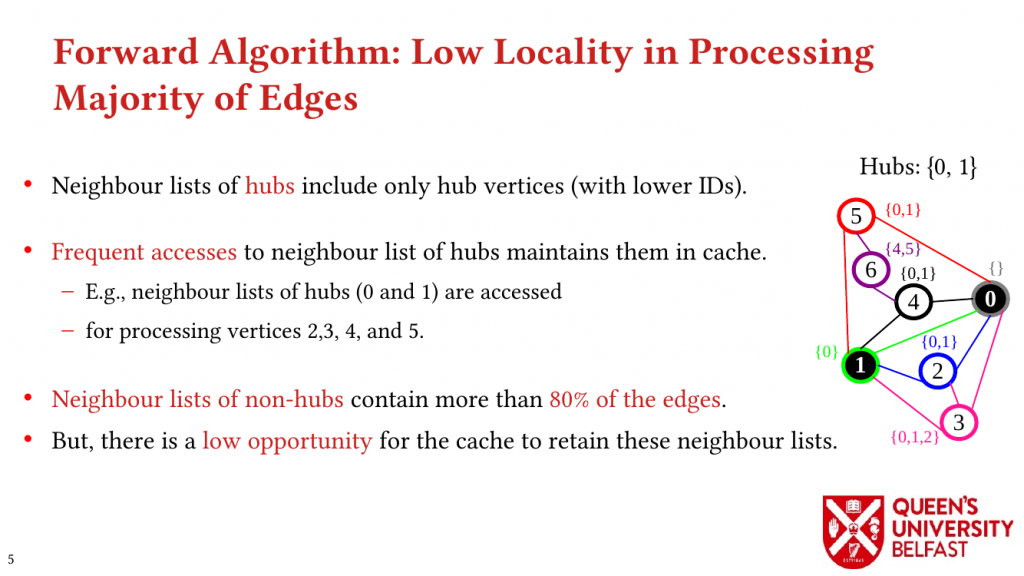
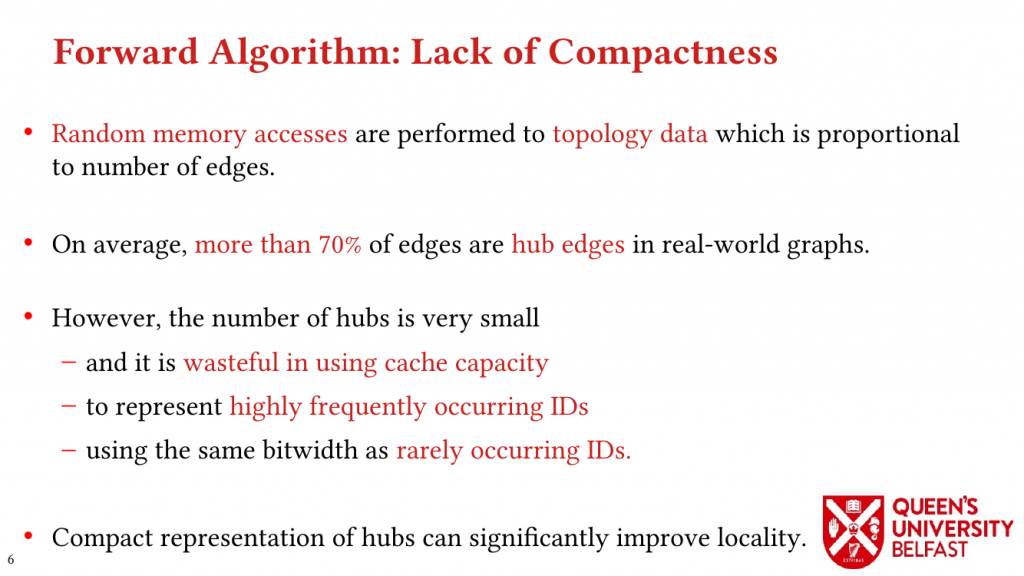
In this paper, we study the implications of the power-law degree distribution of graph datasets on memory utilization in TC and we explain how a great percentage of triangles are formed around a small number of vertices with very great degrees (that are called hubs).
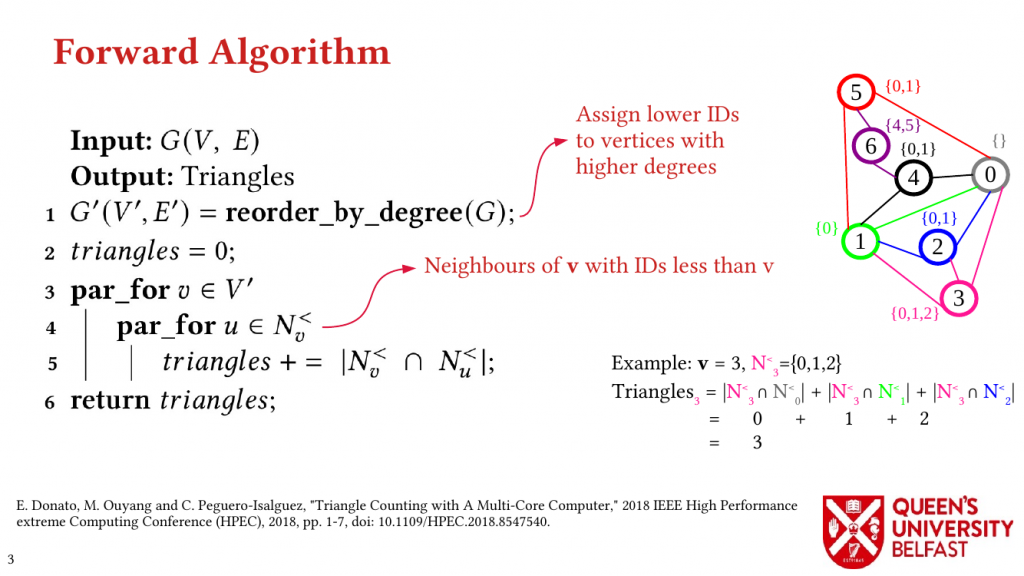
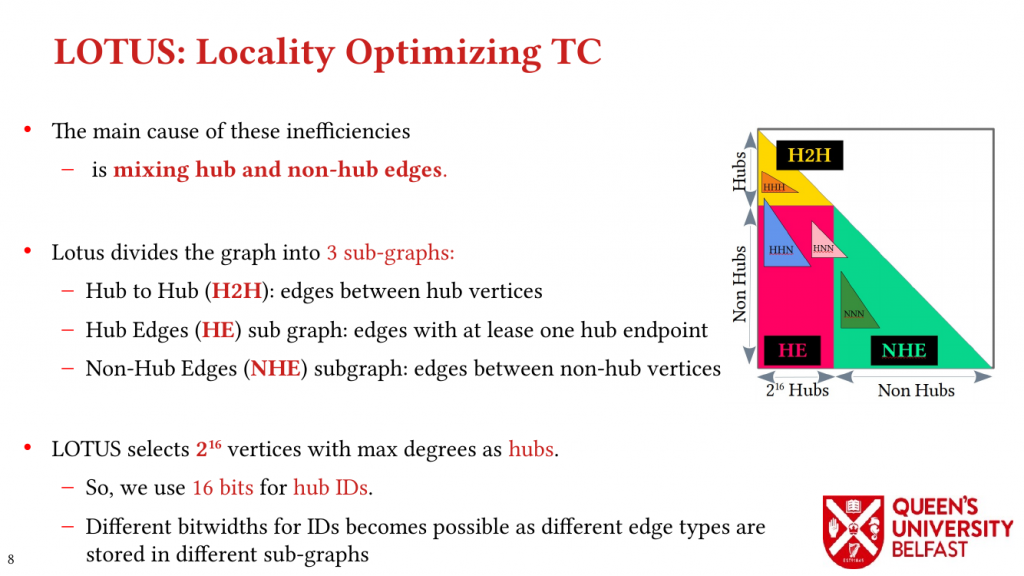
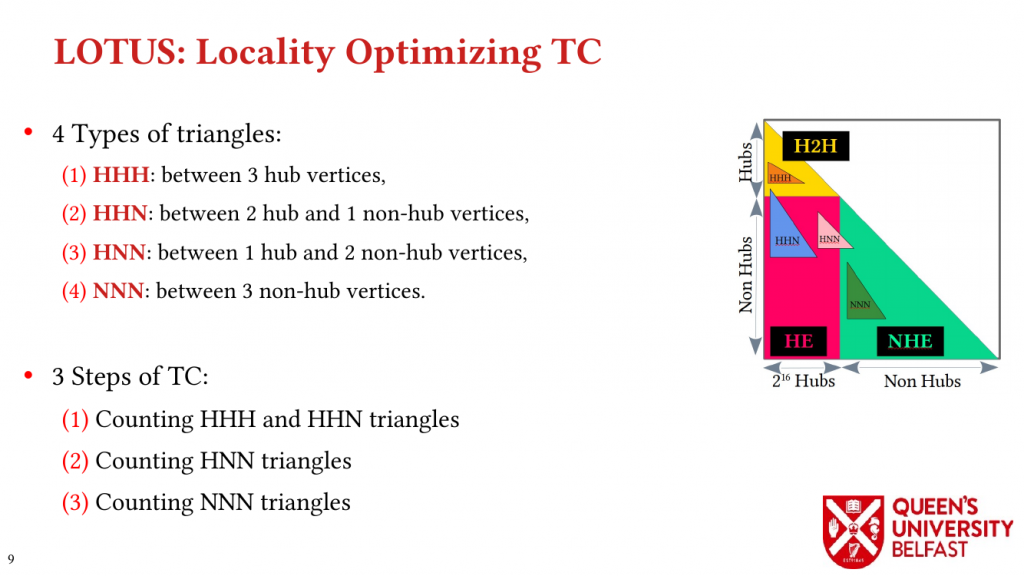
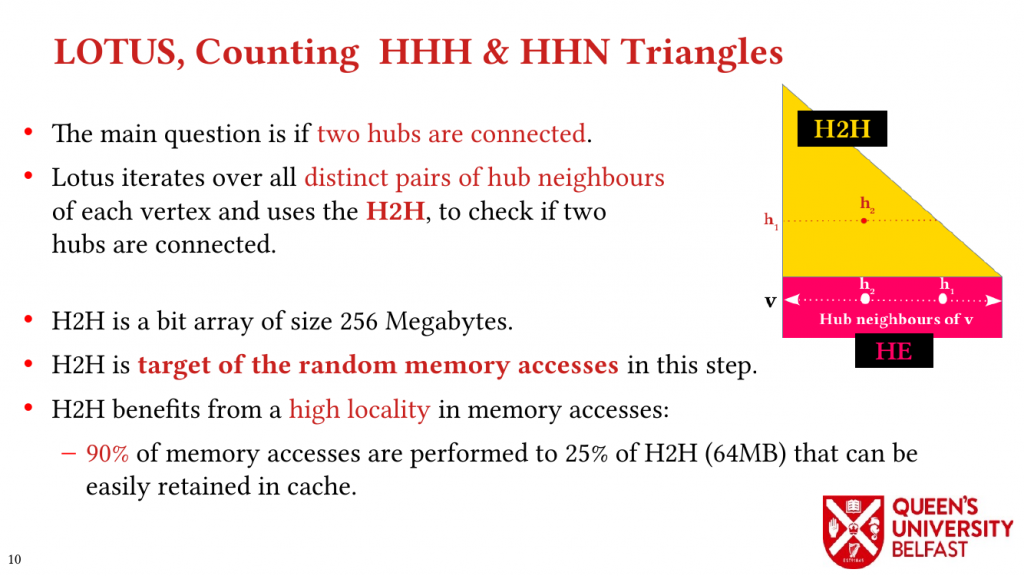
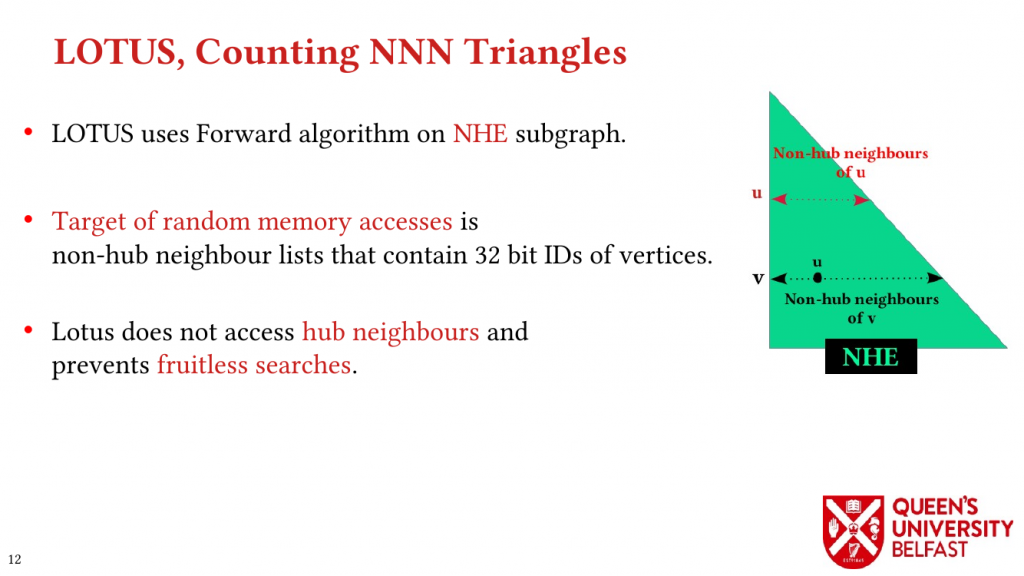
Using these novel observations, we present the LOTUS algorithm as a structure-aware and locality optimizing TC that separates counting triangles formed by hub and non-hub edges. Lotus introduces bespoke TC algorithms and data structures for different edges in order to (i) reduce the size of data structures that are target of random memory accesses, (ii) to optimize cache capacity utilization, (iii) to provide better load balance, and (iv) to avoid fruitless searches.
To provide better CPU utilization, we introduce the Squared Edge Tiling algorithm that divides a large task into smaller ones when the size of work for each edge in the neighbour-list depends on the index of that edge.
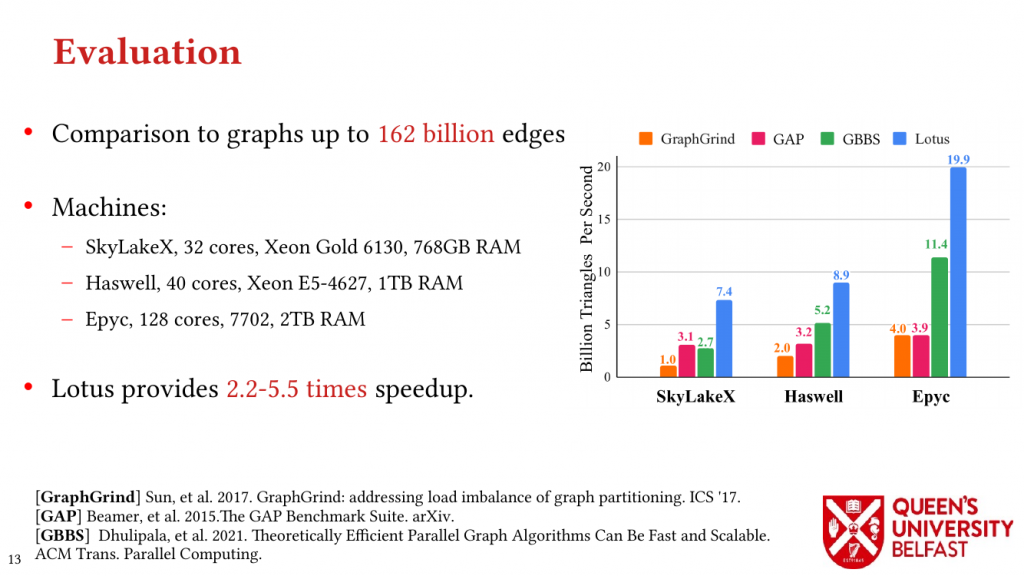
We evaluate the Lotus algorithm on 3 different processor architectures and for real-world graph datasets with up to 162 billion edges that shows LOTUS provides 2.2-5.5 times speedup in comparison to the previous works.
Code Availability
The source-code will be published soon.
BibTex
@INPROCEEDINGS{10.1145/3503221.3508402,
author = {Koohi Esfahani, Mohsen and Kilpatrick, Peter and Vandierendonck, Hans},
booktitle = {27th ACM SIGPLAN Annual Symposium on Principles and Practice of Parallel Programming (PPoPP 2022)},
title = {LOTUS: Locality Optimizing Triangle Counting},
year = {2022},
numpages = {15},
pages={219–233},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
doi = {10.1145/3503221.3508402}
}Related Posts
- On Optimizing Locality of Graph Transposition on Modern Architectures

- Random Vertex Relabelling in LaganLighter

- Minimum Spanning Forest of MS-BioGraphs

- Topology-Based Thread Affinity Setting (Thread Pinning) in OpenMP

- ParaGrapher Integrated to LaganLighter

- On Designing Structure-Aware High-Performance Graph Algorithms (PhD Thesis)

- LaganLighter Source Code

- MASTIFF: Structure-Aware Minimum Spanning Tree/Forest – ICS’22

- SAPCo Sort: Optimizing Degree-Ordering for Power-Law Graphs – ISPASS’22 (Poster)

- LOTUS: Locality Optimizing Triangle Counting – PPOPP’22

- Locality Analysis of Graph Reordering Algorithms – IISWC’21

- Thrifty Label Propagation: Fast Connected Components for Skewed-Degree Graphs – IEEE CLUSTER’21

- Exploiting in-Hub Temporal Locality in SpMV-based Graph Processing – ICPP’21

- How Do Graph Relabeling Algorithms Improve Memory Locality? ISPASS’21 (Poster)