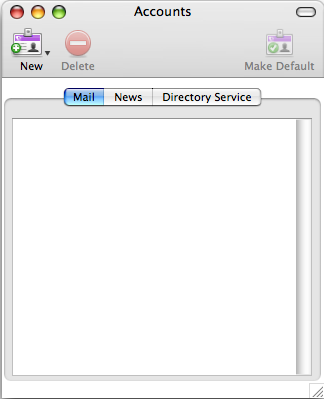
Just an example for future reference of text mangling on unix/linux making use of sed, awk, and grep on a CSV/text file containing names, email addresses etc delimited with a semi-colon ;
cat emailaddresses.csv | grep “@” | awk -F “;” ‘{print $1}’ | sort | uniq | tr [:upper:] [:lower:] | sed ‘s/\@mydomain\.tld\.uk/\ $ main/’ | sed ‘s/\@/ \$ /’ | sed ‘s/^/mj_DLMembers= /’ > processed.txt
So we cat (read out) the contents of our text file ’emailaddresses.csv’ (which I exported from a xls file using Open Office). This is passed through grep so I only get lines which contain the ‘@’ symbol, so only lines containing email addresses – just in case there is a line with column names at the top. We then use awk to cut each of the columns based on the delimiter (; in this case) and ask awk to print out the first column (our email address column).
After that we sort the email addresses into alphabetical order and remove any duplicates using uniq.
The tr (translate) command is used to convert any uppercase characters to lowercase.
Next I have used sed to search (sed ‘s/findthis/replacewiththis/’) each line for the string ‘@mydomain.tld.uk’ (escaping the symbols @ and .) When sed finds a match it replaces it with ‘$ main’ which is what I need for my mailing list. For any other email address other than ‘@mydomain.tld.uk’ I just want to replace the @ symbol with $ so I use sed again for that.
I also need to prefix each line with ‘mj_DLMembers= ‘ so I use sed again, this time finding the start of the line (^) and placing the text string ‘mj_DLMembers= ‘ in there.
Finally I direct (>) the results of this chain of pipes and commands to the file ‘processed.txt’ where I can use it for my mailing list.